Medical imaging is one of the most promising fields for use of AI tools, as pattern recognition and large data sets can enhance human diagnosis (e.g., by radiologists) or even compete with them. A review of AI methodologies was conducted in 2023, concluding that such techniques could help with early disease detection and personalized diagnosis and therapy.
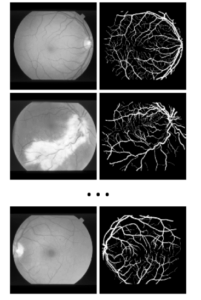
In March 2025, an article in Nature discussed Multimodal generative AI for medical image interpretation. It noted that such techniques could assist clinicians, but that “formidable obstacles remain in validating model accuracy, ensuring transparency and eliciting nuanced impressions.”
Researchers have also focused on specific fields such as rib fracture imaging. A recent rib study focused on criteria for evaluating AI techniques, such as using existing industry standards, and concluding that the “MAIC-10 checklist seems to be a valid evaluation tool for assessing the quality of such studies.” In another recent study, a researcher in Poland reviewed applications of AI in medical imaging for cancer detection.
Some models focus on capturing uncertainty to assist clinicians and researchers, as shown in this research paper.
In view of these studies and reviews, it appears that researchers and the medical device industry are attempting to apply several principles provided in 2024 by the FDA for good machine learning practice. Such principles include focusing on “performance of the human-AI team” and testing during “clinically relevant conditions.” However, a review of the resources described here reveals that AI tools often provide complex outputs, so the quest continues to apply another of these principles: providing users with “clear, essential information.”